Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: Dec 28, 2021
Post-hoc test
In statistics, a post-hoc test typically refers to a test conducted after analysis of variance (ANOVA). “Post-hoc” means “after this” in Latin.
Becuse the null hypothesis of ANOVA is that there is no difference among group means, ANOVA does not analyze differences between group means. Post-hoc tests are used to test the differences between group means in multiple comparison.
Below is a typical figure of multiple comparison [1].
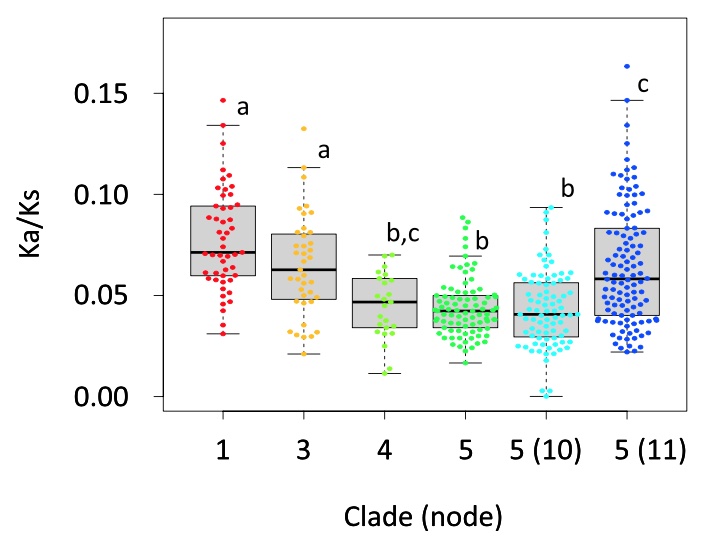
Common post-hoc tests include the following.
Tukey HSD |
HSD stands for “honest significant difference.” |
Comparison between the control group vs. several experimental groups. |
|
Not recommended because of the high probability of type I error. |
Definitions in the literature
- Post-hoc tests may be a priori (comparisons that were planned before the ANOVA was performed) or a posteriori (run after the ANOVA is performed and run only if the F statistic from the ANOVA is significant). These types of contrasts are tested using different methods [2].

