Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: Jan 21, 2023
ANOVA, analysis of variance
ANOVA (analysis of variance) is a statistical test to identify significant differences (see P value) between categorical groups using a variance.
ANOVA is generally used for data containing more than three categorical groups. Depending on the number of factors, one-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA are commonly used.
One-way ANOVA
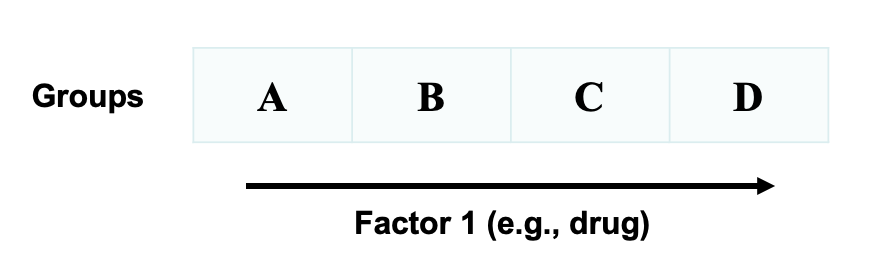
Two-way ANOVA
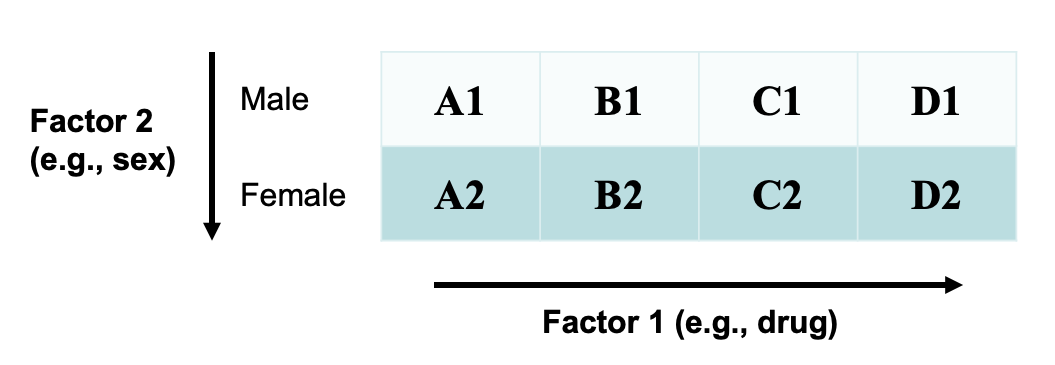
Some important features related to ANOVA includes:
- ANOVA is a parametric method that assumes a normal distribution.
- ANOVA determines whether there is a significant difference between groups, but does not show that which groups are significantly different. A post-hoc test should be applied to detect the inter-group differences.
Definitions in the literature
- An ANOVA test is a statistical test used to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between two or more categorical groups by testing for differences of means using a variance [1].

