Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: Nov 8, 2020
Mutation
A mutation is a heritable change in genetic information encoded by DNA or RNA detected in less than 1% of a given population.
When the variation in DNA sequence is observed in more than 1% of a given population, it is called a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
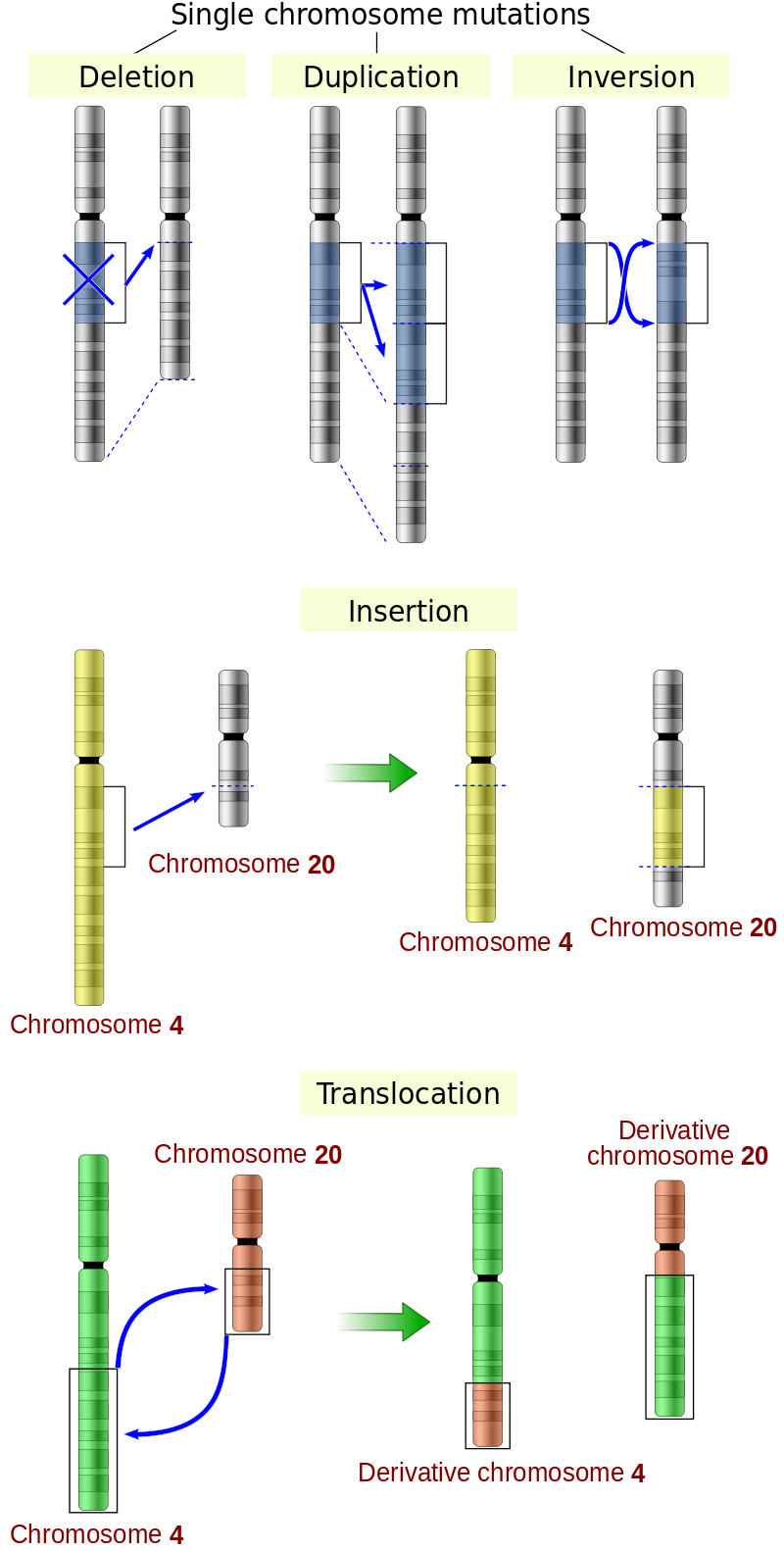
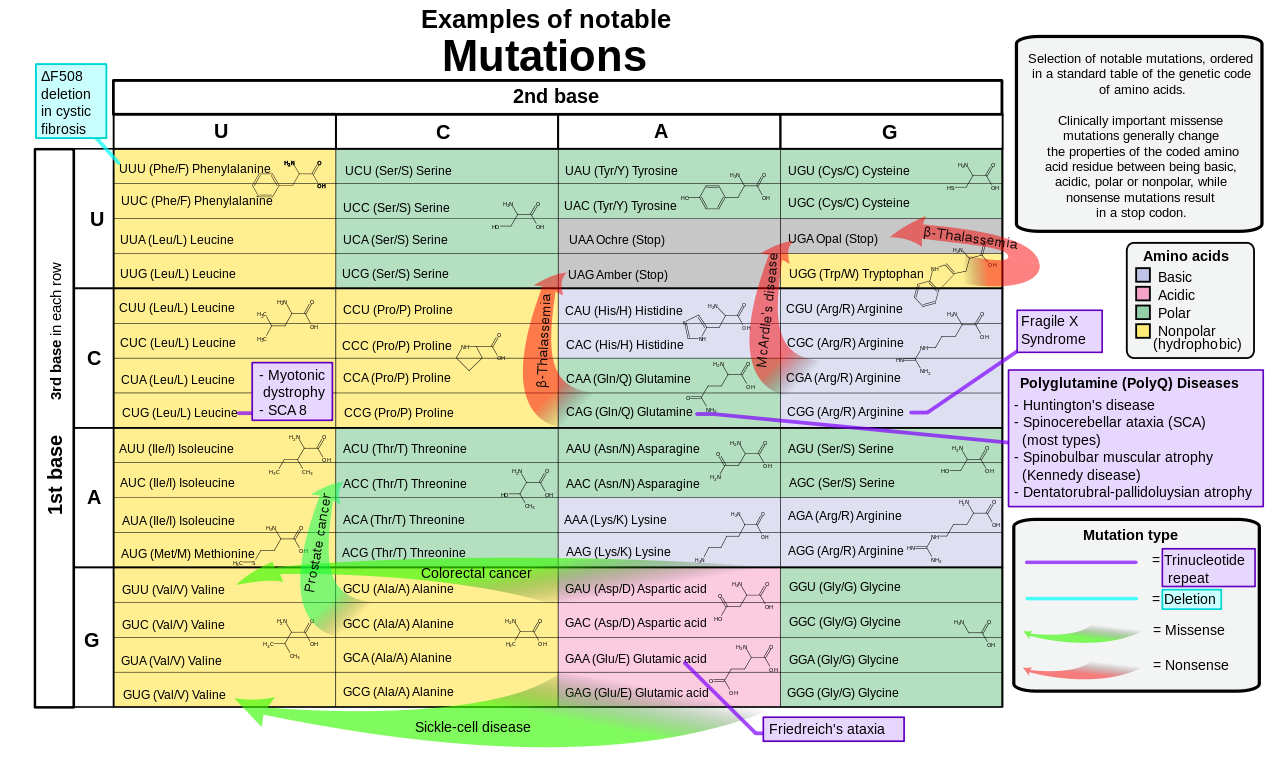
Mutations are classified by their effects on genotypes and phenotypes, type of cells, and molecular nature. Examples are shown in the figure below – missense mutation, nonsense mutation, and silent mutation:

Other types of mutation:
- Transition: Base substitution from a purine to a different purine or a pyrimidine to a different pyrimidine
- Transversion: Base substitution from a purine to pyrimidine or vice versa.
Definitions in the literature
- Heritable change in genetic information [1].
- A change in the base sequence of DNA in a gene; often used to refer to a genetic change that is significant enough to alter the appearance or function of the organism [2].
- Nowadays DNA variants are called as differences in comparison to a reference. In a sequencing project Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms ( SNPs) and DNA mutations are defined as DNA variants detectable in >1 % or <1 % of the population, respectively [3].
Images
Click to see full-size images. All images are Public Domain.