Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: Oct 19, 2020
Open reading frame
An open reading frame (ORF) is a continuous sequence of DNA or RNA, when translated into amino acids, contains no stop codons.
As shown in the "Definitions in the literature," there are multiple definitions of ORF that are conflicting to each other – whether we can use this word for both DNA or RNA, and whether a stop codon is included in ORF.
This dictonary consideres that the definition in National Human Genome Research Institute [2] is clear and reasonable, in which a stop codon is not included in ORF.
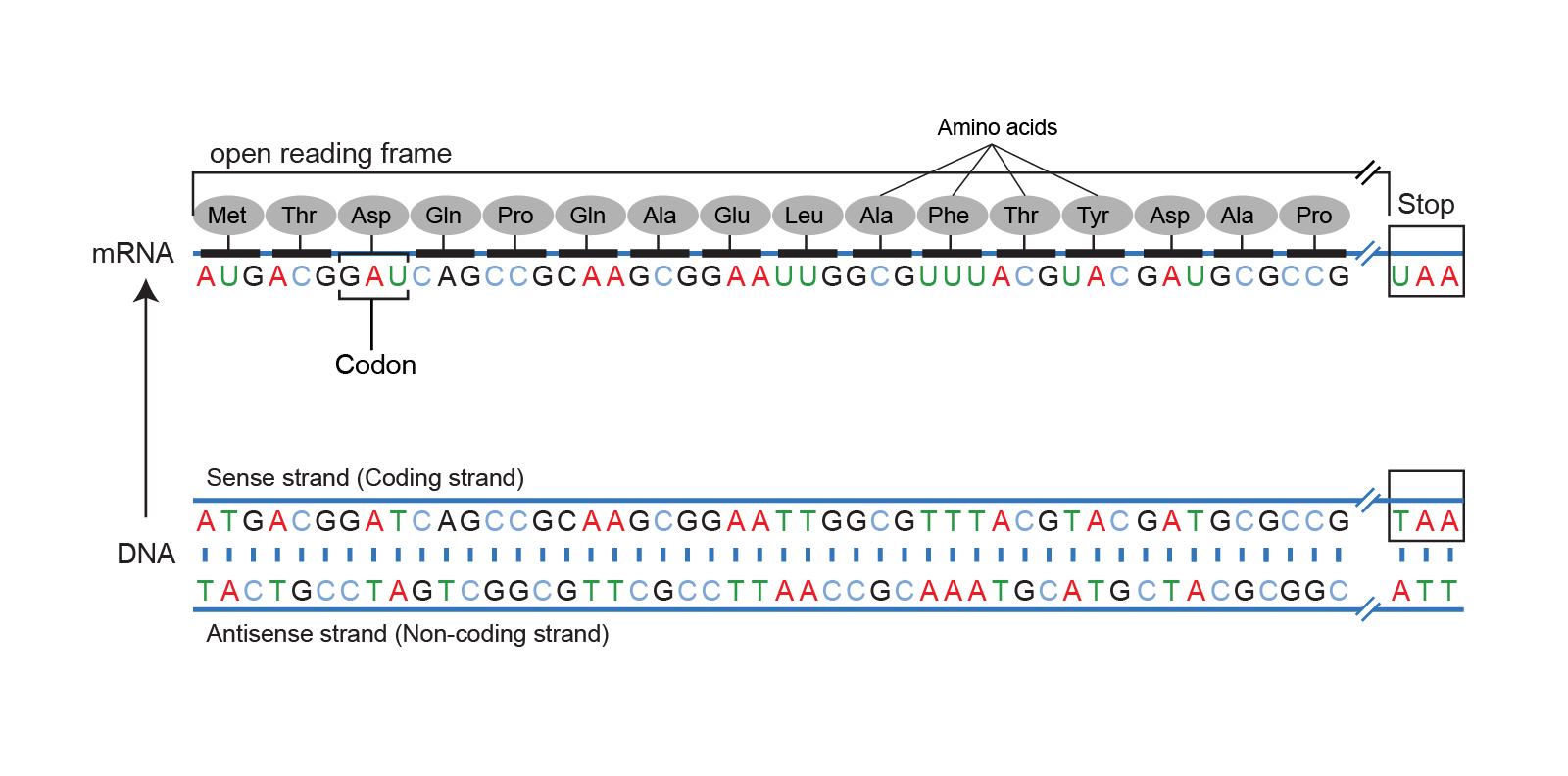
Figure cited from [2].
Definitions in the literature
- Continuous sequences of DNA nucleotides that contains a start codon and a stop codon in the same reading frame; is assumed to be a gene that encodes a protein but, in many cases, the protein has not yet been identified [1].
- An open reading frame is a portion of a DNA molecule that, when translated into amino acids, contains no stop codons [2].
- A DNA sequence that has the potential to encode a protein sequence. An ORF begins with a start codon (ATG) and ends with a stop codon (TAA, TAG, or TGA) in most species [3].
- An ORF is the length of DNA or RNA sequence that has no stop codon signals in it [4].

