Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: Jul 23, 2022
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is an array of electron carrier molecules and other supporting molecules embedded in biological membranes.
The ETC embedded in mitochondrial inner membrane is called the respiratory chain (Fig). Chloroplasts also contain the photosynthetic ETC in the thylakoid membrane.
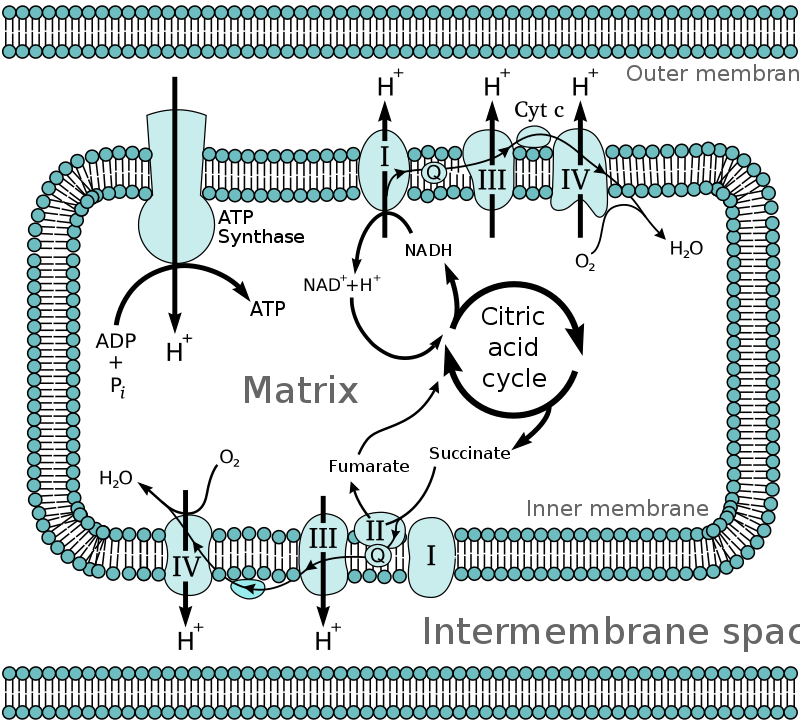
Using the energy from mitochondrial respiratory chain, ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and phosphate. This process is called oxidative phosphorylation. The oxidative phosphorylation is thus coupled to the respiratory chain.
Definitions in the literature
- the series of electron transport protein embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that accept high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 and transfer them in stepwise fashion to molecular oxygen [1].
- Array of membrane-bound enzymes and other molecules that accept and give up electrons in sequence, thus releasing the energy of the electrons in small, usable steps [2].
- A series of electron carrier molecules, found in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and the inner membrane of mitochondria, that extract energy from electrons and generate ATP or other energetic molecules [3].
- A sequence of biochemical reduction-oxidation reactions that effects the transfer of electrons through a series of carriers. An electron transport chain, also known as the respiratory chain, forms the final stage of aerobic respiration. ... An electron transport chain also occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts in photosynthesis [4].
Definition in [1] appears inappropriate since this does not contain the photosynthetic ETC.

