Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: May 6, 2024
- May 3, 2022
Carotenoid
Carotenoids are a group of lipid-soluble pigments structurally related to terpenes. Carotenoids have various colors such as yellow, orange, red, and brown, and are commonly present in animals and plants.
Carotenoids generally contain 40 carbons and 9 double bonds at the center part of the molecule. The figure below is the structure of isorenieratene, a carotenoid found in green sulfur bacteria.
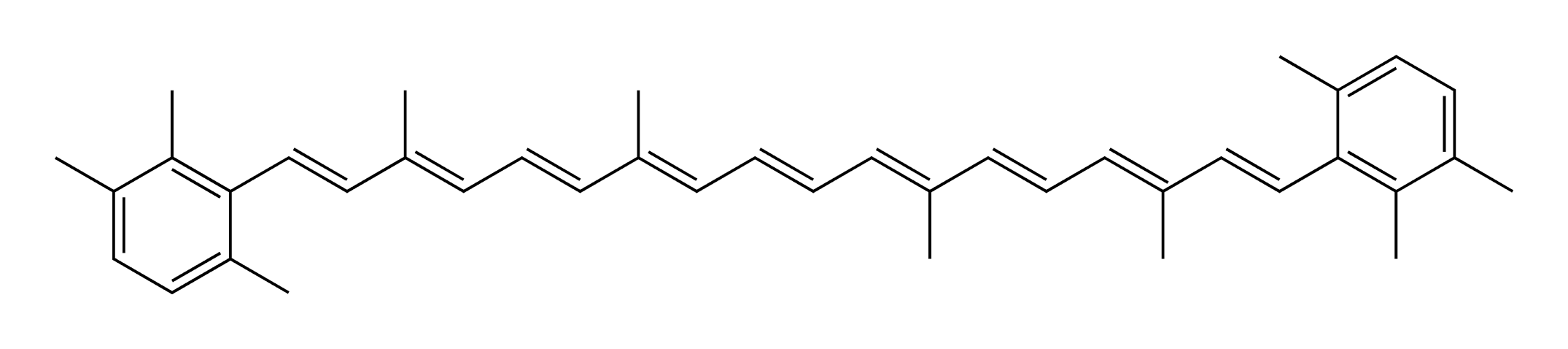
There are several subgroups of carotenoids that have a different basic structure.
Some examples of carotenoid include the lycopene (red pigment of tomato) and astaxanthin (orange pigment of shrimps and salmons).
Definitions in the literature
- Any of a group of yellow, orange, red, or brown pigments chemically related to terpenes [1].
- Carotenoids are a family of compounds of over 600 fat-soluble plant pigments and provide much of the color we see in nature [2].

