Search Dictionary
Version history
- Current: Jan 18, 2024
- Old versions
Buffer
A buffer solution is a solution containing a conjugate acid-base pair of a weak acid or a weak base.
Buffers are resistant to changes in pH; i.e., buffer components can release or absorb protons in the solution, helping to maintain the pH within certain range.
Example: When acids are added, components of the phosphate buffer absorb the proton, maintaining pH.
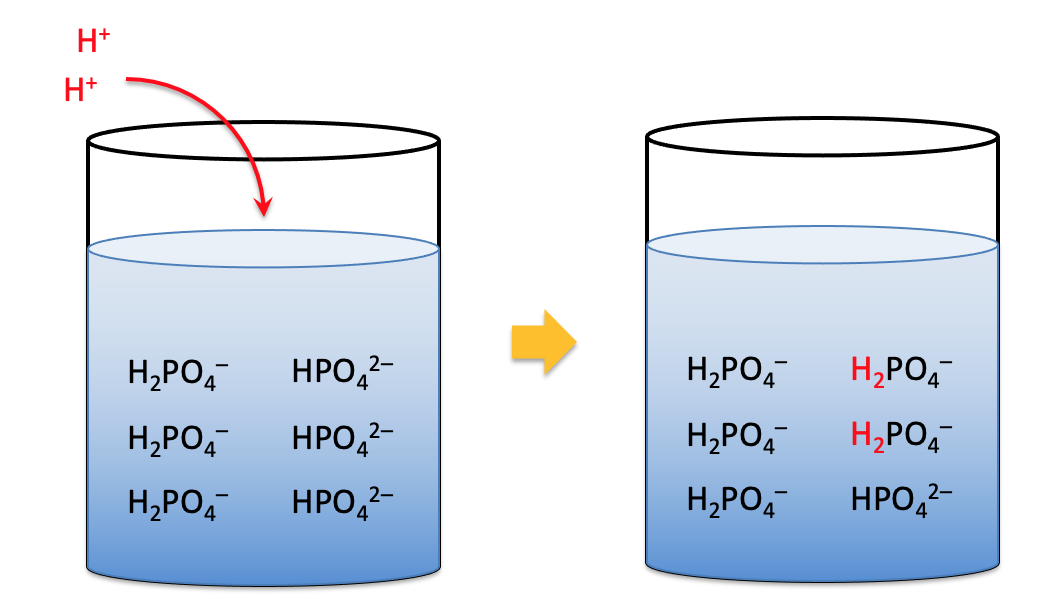
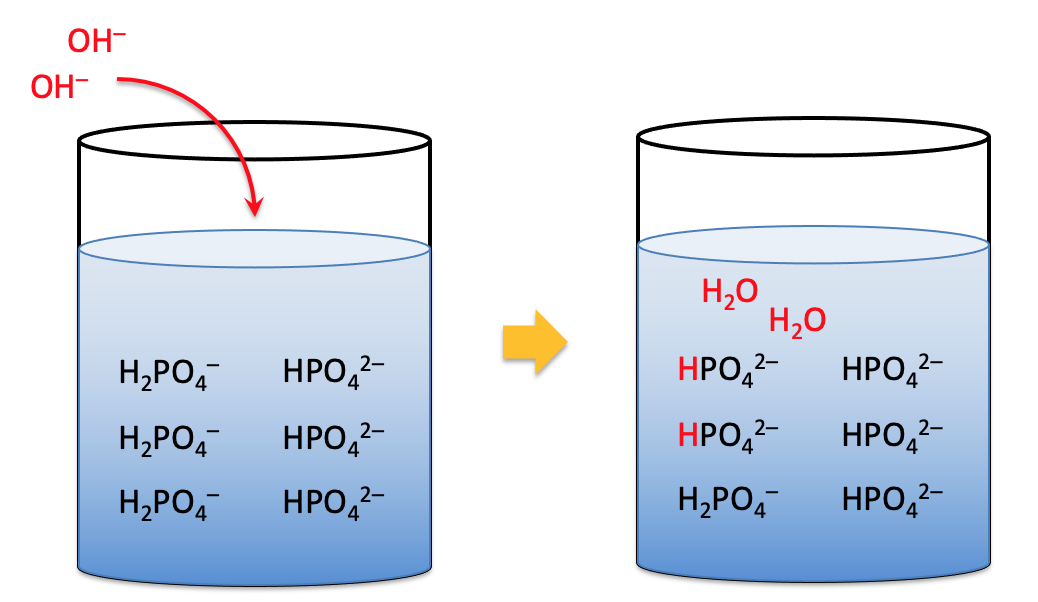
The same buffer can maintain the pH when bases are added.
Definitions in the literature
- Buffers resist a change in pH when protons are produced or consumed. Maximum buffering capacity occurs ± 1 pH unit on either side of pKa. Physiologic buffers include bicarbonate, orthophosphate, and proteins [1].
- buffer solution: a solution containing a weak acid or base and its salt (the conjugate base or acid) that is resistant to large changes in pH upon addition of strong acids or bases [2].

